One area where fees and benefits can vary significantly is in the annuity space. For example, annuities with a Guaranteed Lifetime Withdrawal Benefit (GLWB) feature – which allows access to the annuity contract value (i.e., are revocable) and guarantees a minimum level of lifetime income (which in some cases could even increase) even if the underlying account value goes to zero – can come with a range of features that add additional costs. And while GLWBs have traditionally offered an annual ‘step-up’ provision (that can increase the income/benefit base used to determine the income level), more recent products only offer a step-up only once, at retirement. These ‘GLWB-Lite’ products with fewer step-ups come with reduced fees compared to ‘regular’ GLWBs, but advisors might wonder whether the reduced costs are outweighed by the more limited benefits.
According to an analysis conducted by Blanchett, while the expected aggregate value of the products (lifetime payments plus any residual balance available for heirs) is similar, the ‘regular’ GLWB dominates based on lifetime income (while there is a larger residual balance leftover with the ‘GLWB-Lite’). And so, because individuals typically buy annuities for the income benefits as a form of longevity insurance (rather than as a tool to maximize the size of legacy gifts), it likely makes more sense for these individuals to purchase the ‘regular’ higher-cost GLWB if they’re going to pursue such income guarantees at all (and perhaps earmark some of the non-annuitized portions of their portfolio for a legacy benefit).
Ultimately, the key point is that it is important for advisors to look beyond fees and understand client goals when analyzing potential investment products. And this is especially true in the case of annuities with GLWB features, where ironically seeking the lowest-cost option could negate much of the benefit of buying an annuity in the first place!

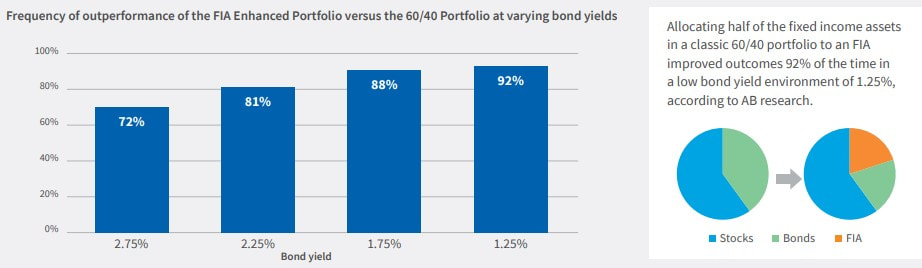
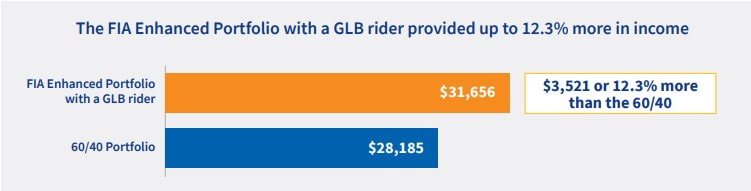
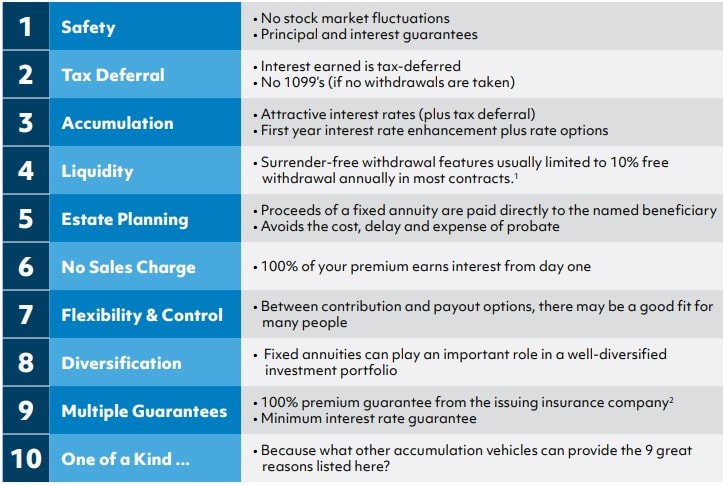
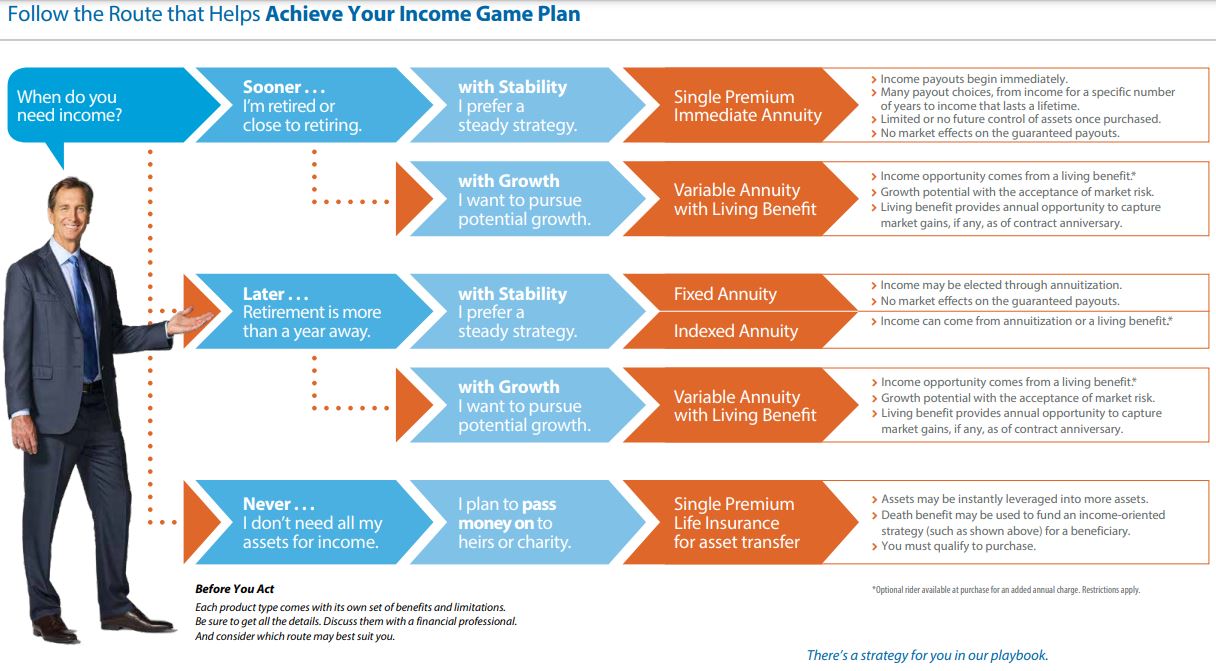
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
